ah teaches graphic design (Context Shmontext lecture)
Context Shmontext
Lecture outline
Understanding how context and audience plays into understanding our design. Lecture slides will be made available on the day of the lecture (October 21/22).
In preparation for lecture...
Please close up any laptops, cellphones, Commodore 64's, Telstar Arcades and other 'beep-boop' devices.
P1 grades
Your P1 grades will be released to you by end of day Wednesday. If you have any questions or concerns with your grades please follow-up with Andrew.
Ninta & Zi will be unable to discuss grades.
Today's critique
Our approach
You choose the critique approach, but be prepared to explain why.
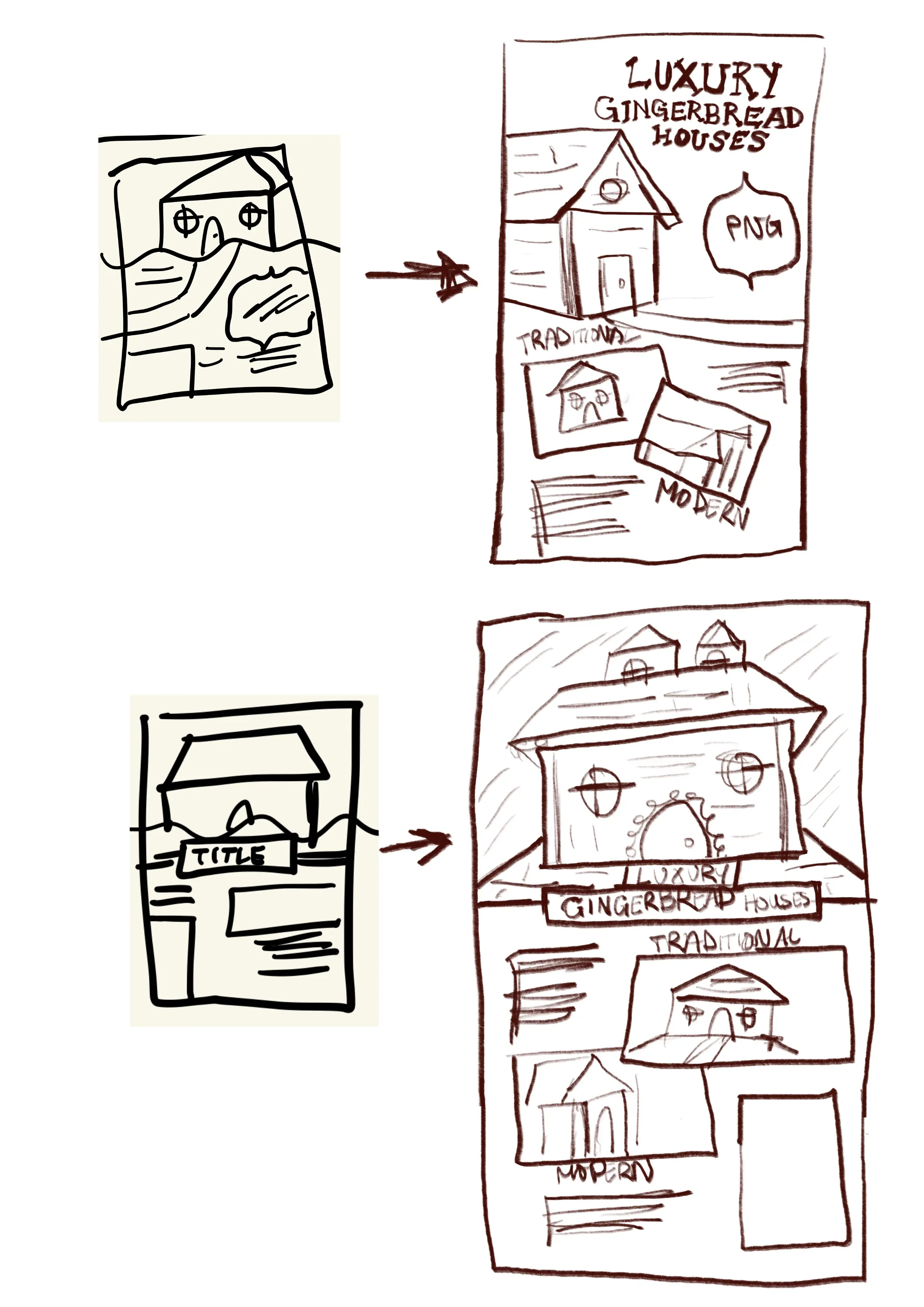
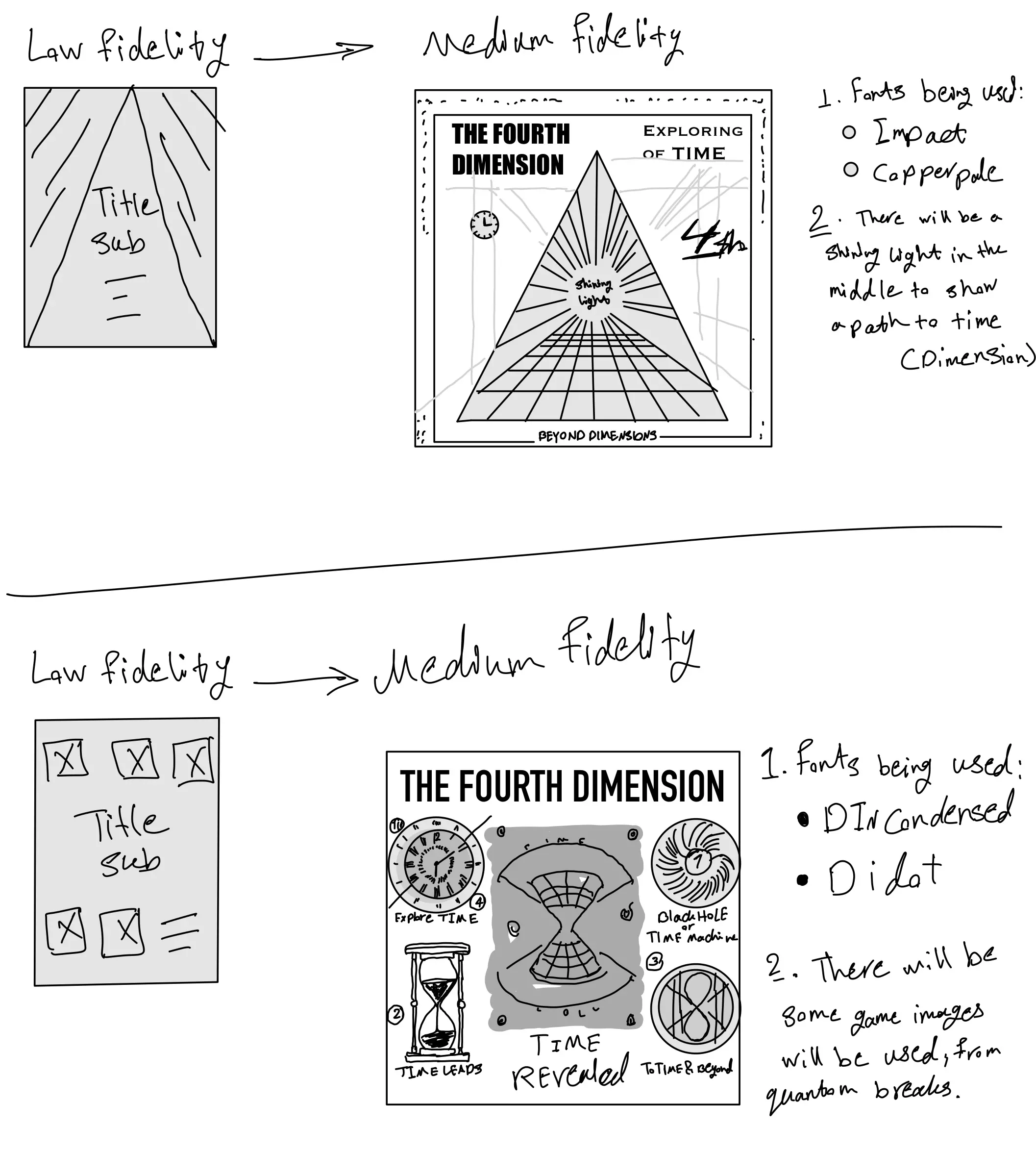
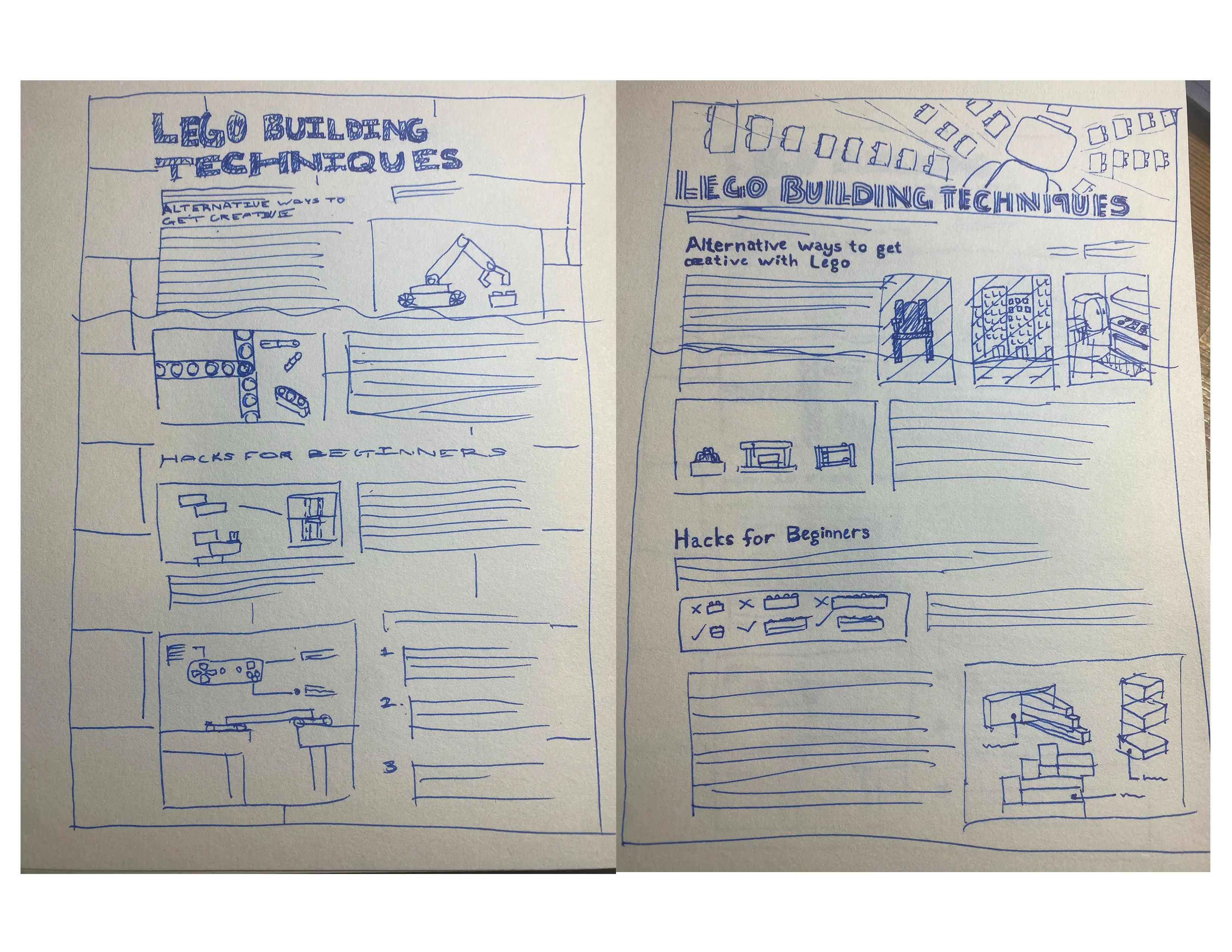
Context Schmontext
Context
The relationship between a user and all the parts of their environment, as they perceive it.
Layers of Information
Within this class I would like you to think about three layers of information:
- Physical: A user's relationship to their environment.
- Semantic: Messages or meaning established for others.
- Digital: Encoded/computer-centric messaging.
Semiotics
Put simply, is the study of signs.
Signs Aren't Just Signs
(in semiotics)

Signs
The Saussurean model
Have two parts:
- The Signifier, was the psychological impression of the sound.
- The Signified was a concept.
Signs
The modern model
Have two parts:
- The Signifier; is the material form we can physically sense.
- The Signified; is the mental or psychological associations.
One Signifier, Many Signified
Signifier
Signified?
One Signifier, Many Signified
Signifier
Signified
- Dog
- Fuzzy
- Cuddly
- Noisy
- Slobber
Abstract Relationships
Signs are relational; we only understand cat in relation to dog.
Icon, Index, Symbol
The Peirce addition
These define three approaches that we take to defining the relationship between the signifier and signified.
- Icons: Signifier resembles the signified
- Index: Signifier directly connected to signified and a link can be observed
- Symbol: Signifier is arbitrarily related to the signified
Icon
Index
Symbol
Dog
How We Talk About Meaning
How might we talk about this as an:
- Icon?
- Index?
- Symbol?

Why These Are Important
Icon, index and symbol illustrate different ways we can interpret meaning of a given message. It also help assess how clearly that relationship may be understood.
Substance and Form
Hjelmslev and semiotics
"...there can be no content without an expression, or expressionless content; neither can there be an expression without a content, or a content-less expression."Louis Hjelmslev
Understanding Meaning
A bit more semiotics
Denotation is a literal or descriptive meaning of an item.
- What is this a picture of?
- What typeface is this?
- What is this colour?
Connotation is a individual or cultural meaning of an item.
- How does this picture make you feel?
- What does this typeface remind you of?
- How does this colour effect your opinion?
DENOTATION
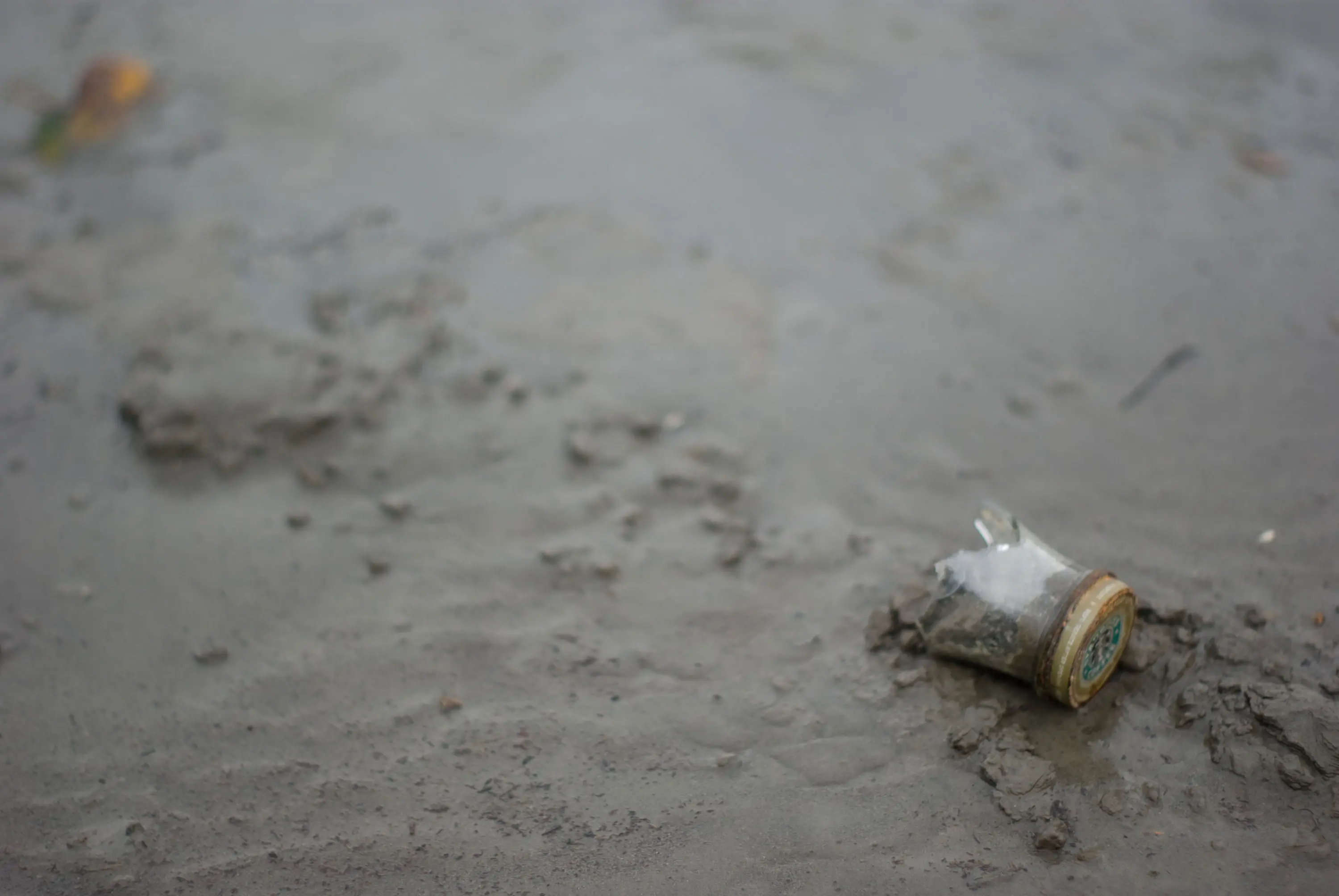

What are the denotations of this photo?

What are the connotations of this photo?


Metaphor

How do the denotations/connotations of this photo compete?
Obvious vs. Obscure
The designer's challenge
Contexts
Consider:
- How is it accessed?
- Environment used in?
- Time of use?


Composing Without Grids
Composing without grids is not an excuse to do whatever you want.
Considerations include:
- Making a center of interest
- Directing the eye and rhythm
- Balance, unity and harmony
Center of Interest
A strong center of interest often involves use of contrast and balance to focus our attention.

Directing the Eye + Rhythm
Using position, emphasis, and the visual cues within your composition can help direct the eye through.

Photos as structure
Remember that the photos you choose can strongly suggest a structure.
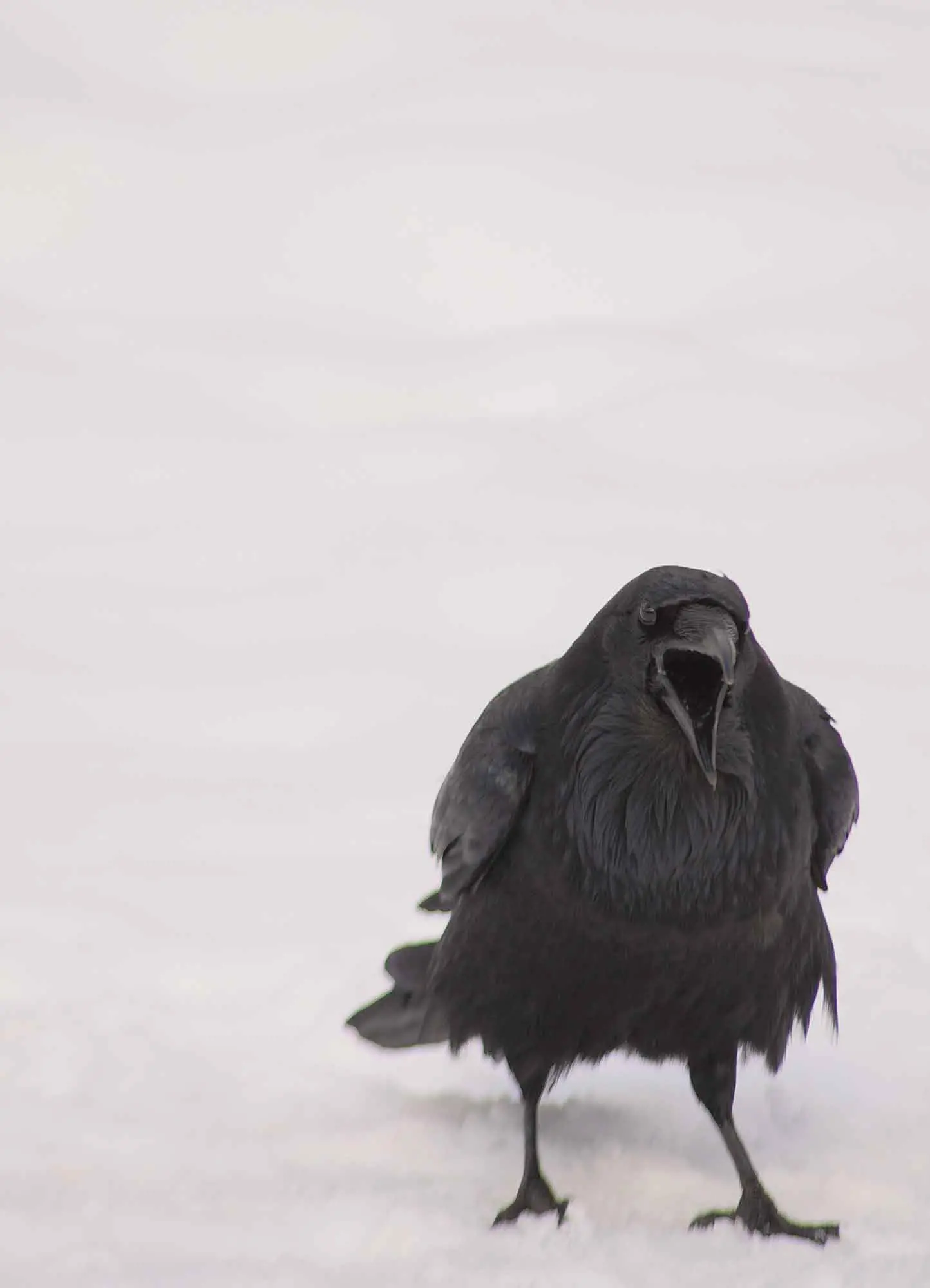

Balance, Unity and Harmony
Ensuring that we perceive the composition as one piece.

Bring P2 to lecture
We will be doing a mass-crit as part of next week's class. Please bring your P2 deliverables to class for further feedback.